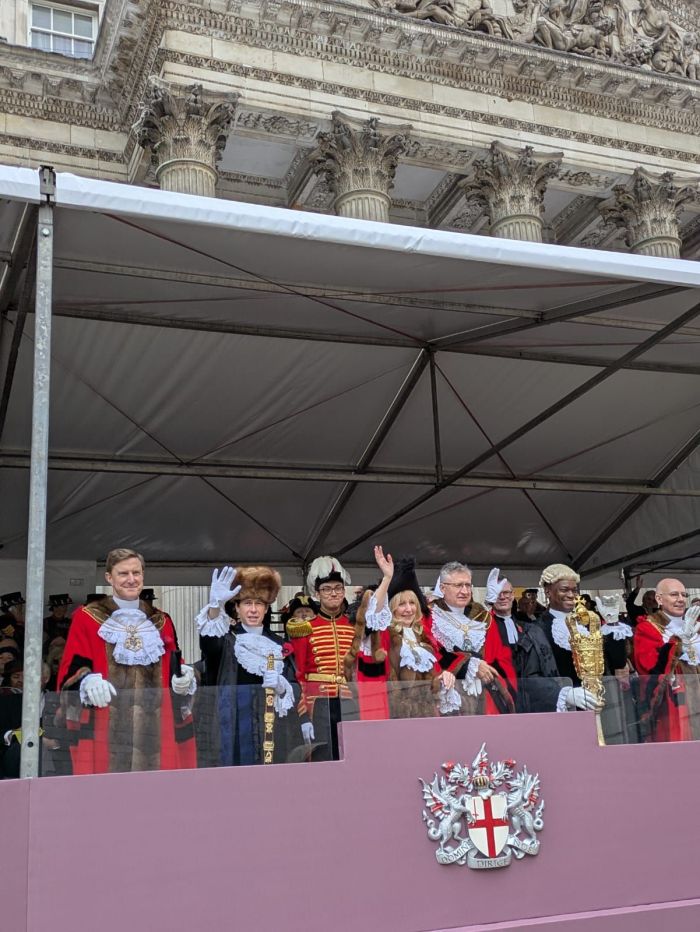
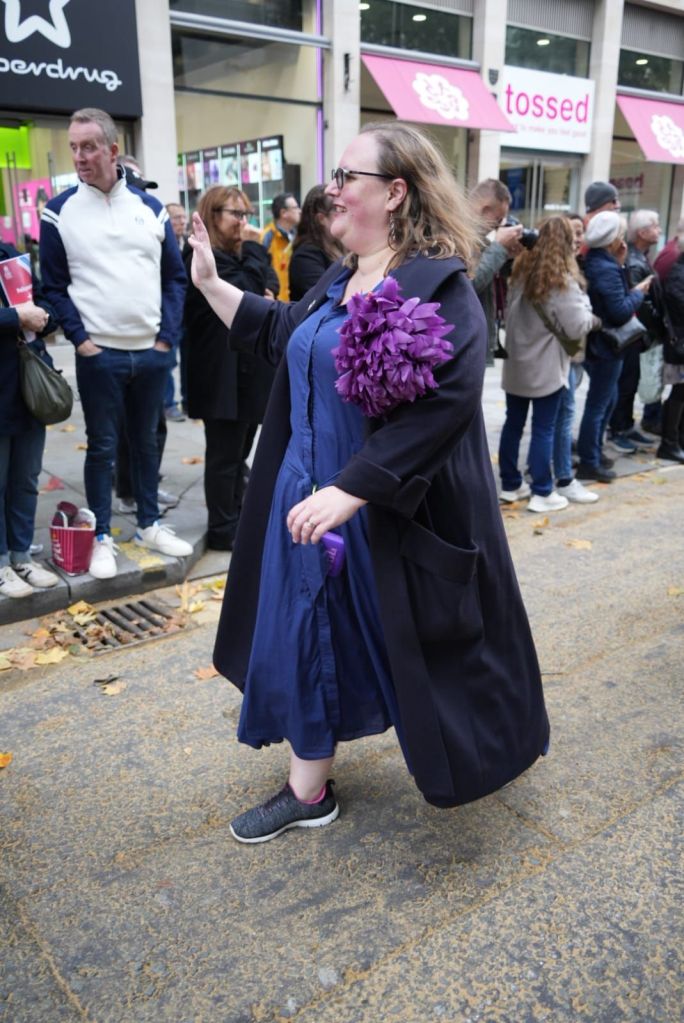
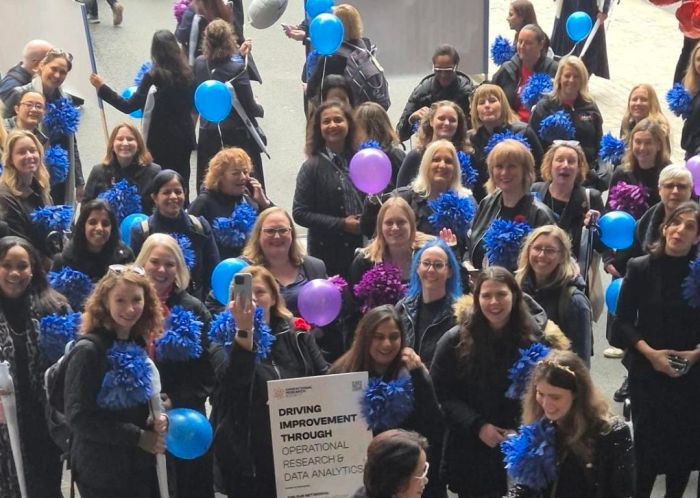
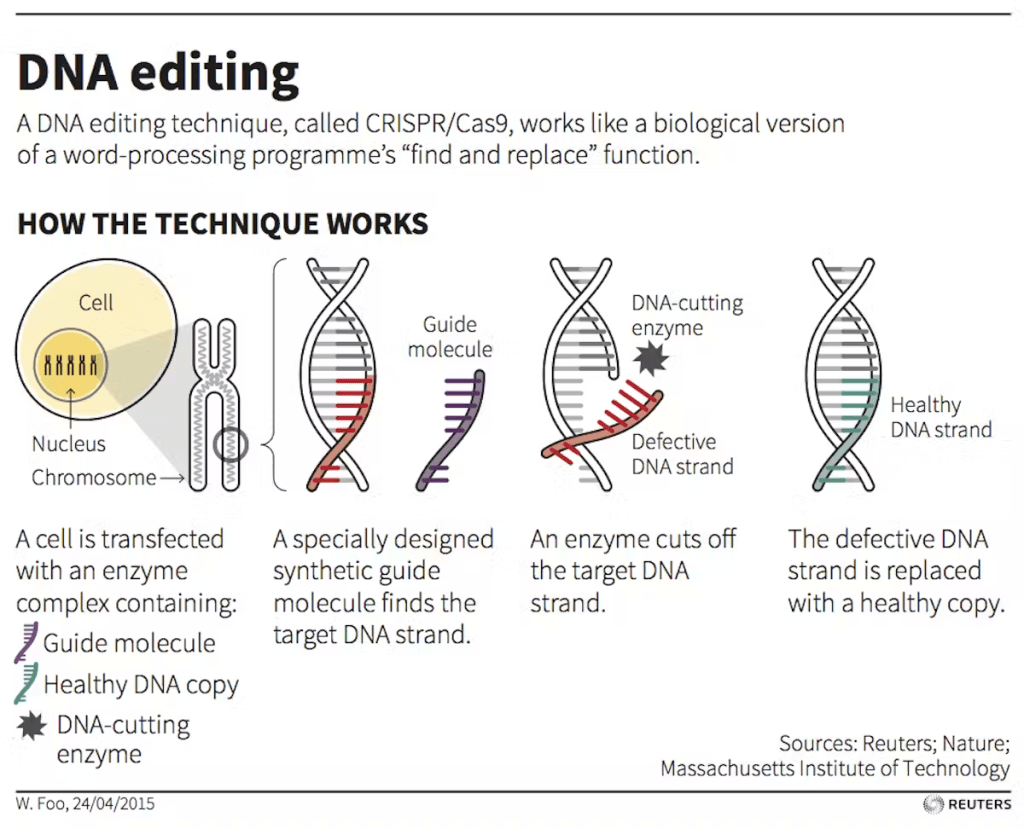
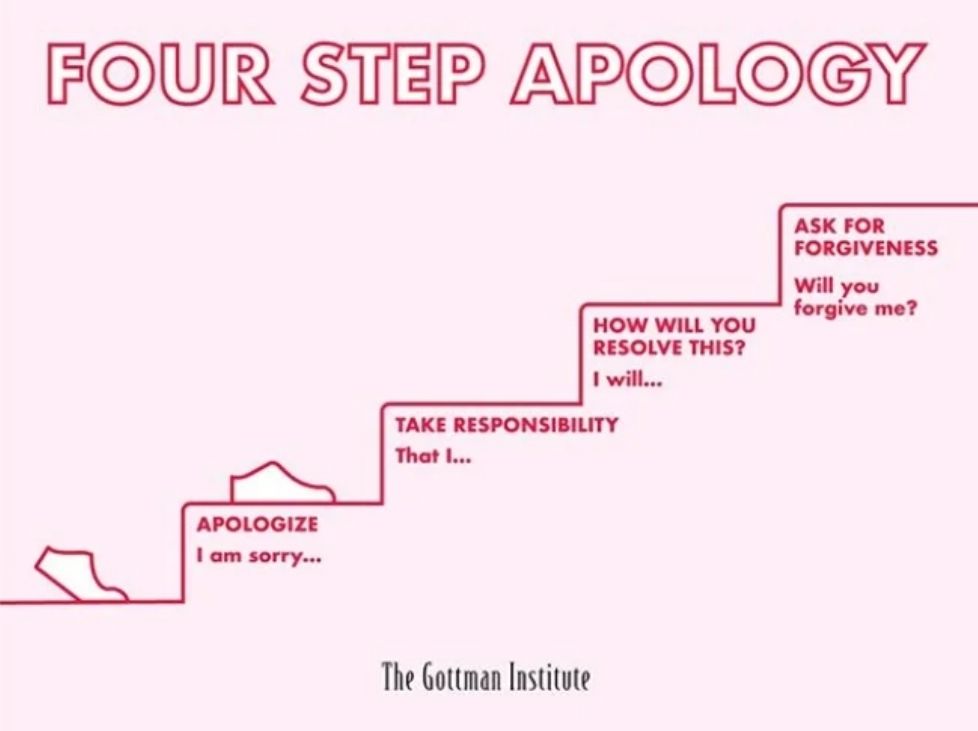
On 8 November 2025, 200 women from across the worlds of tech and health walked together in the Lady Mayor’s Show answering Dame Susan Langley’s 697 call for change. They formed part of 697 women walking to support the historic shift that Dame Susan is introducing as the 697th Lord Mayor of London.
This post was just going to be about the privilege of being involved in walking in such an amazing historic event, but then an article was published by the New York Times on the 6th November which both changed what I wanted to say, the context of why I think the walk was important, and also required a few weeks of calm reflection before I felt I was ready to write it.
The article was called “Did Women Ruin the Workplace? And if So, Can Conservative Feminism Fix It?” Needless to say it garnered quite the response on social media and across the internet:
If you, like me, don’t have a New York Times subscription, this article summarises it pretty well: https://www.glamourmagazine.co.uk/article/conservative-feminism-new-york-times
Reading and processing my response to both the article and the coverage led me down a number of rabbit holes, both about the history of women in the work place, and women’s right to equality linked to both work and the money acquired as a consequence of that work. Some of which shocked me.
History is important, as it leads us to the present. It also means that we acknowledge the fight it took to get to our current ‘normal’ and prepares us for the role we need to play to make the changes for those that will follow. So, before I talk about how this ties into the Lady Mayor of London and the Lead WITH Us movement, I thought it was important context to share.
Why does having women in the workplace matter?
Access for women to work has not been an easy path, many women had to stand up, be seen, and be counted in order for progress to occur. In my mind, most of this change happened when Queen Victoria was on the thrown, but that assumption was far from correct. Here are some key points of that history:
- Elizabeth Garrett Anderson was the first female doctor allowed to train and become legally qualified in 1865, no British hospital would accept her qualifications however and so she studied in Paris to gain her formal degree and was eventually admitted to the British Medical Register in 1870. She then worked to bring in the Medical Act of 1876 to formally open the medical profession to women, and co-founded the London School of Medicine for Women which now forms part of UCL

- The first female MPs were permitted following the Parliament Qualification of Women Act in 1918. The first woman elected was Constance Markievicz, but she didn’t actually take her seat. The first woman to actually sit as an MP was Nancy Astor. Despite this, women could not sit within the House of Lords until after the Life Peerages Act 1958 that permitted Baroness Swanborough, Lady Reading and Baroness Wooten to take their seats
- Women were not allowed to serve as magistrates or on juries until 1919. Even when the law changed however, juries remained predominantly male for another 40 years. The same act permitted women the right to undertake professional careers, such accountant, or vet, but women did not have protection for the income they earned until much later

- Women were not allowed into ground combat roles in the UK military until 2016, with the RAF opening up roles in 2017, and the wider military 2018. Women had served in combat prior to this, but were banned from serving in front line military units
Unless you have women in the rooms where decisions are made the voices of women will never truly be heard. This is why the role of women in the workplace is so key. Much of the change that has occurred has been incremental, as it was only when women made it into positions where they could influence change, that that change occurred for the wider population. Even when laws change, culture change takes longer, and so embedded change requires conscious effort for decades after the first shift occurs. We have all seen recently how quickly rights can disappear that had been considered to be part of day to day life, and so there is a continuing need to not take rights that were hard earned for granted.
Why is women working important for both them and society?
Access to work supports both financial and societal freedom, supporting autonomy and decision making. When looking into the history of how work placed change impacted on financial autonomy I was pretty shocked by the fact that the timeline for some of these changes occurred within my lifetime.
- The first petition for women’s suffrage in parliament was in 1867, but it wasn’t until Parliament Qualification of Women Act of 1918 (the same act that permitted female MPs) that eligible women were granted the right to vote. It wasn’t until 1928 that the Equal Franchise Act passed that gave women equal voting rights to men, making 15 million women eligible to vote

- The Married Women’s Property act passed within the UK in 1870, which allowed women to become the legal owners of any money they earned. Women could not however inherit property on the same terms as men until 1922, when a property act change meant that that a husband and wife could inherit each others property. Prior to this, women had to give up all rights to their property when they married
- Women had no legal right to equal pay until the 1970 Equal Pay act which came into being after 850 female workers went on strike at Ford Motor factory in Dagenham. Even so this allowed men to be paid no more than 15% more than women. The Equal Pay amendment act (1983) allowed women to be the paid the same as men for equal work – the pay gap however remains ~15%
- It took until 1975 for women to be allowed bank accounts in their own names with no counter signatories (when the sex discrimination act came into law). Before then, although no law forbade women from having their own accounts, but many banks and financial institutions still required a male guarantor to open accounts, access credit, or get a mortgage

- It was not until 1982 that the law changed to mean it was illegal to refuse to serve a woman a drink if she was unaccompanied by a man
- Statutory maternity introduced in 1987 permitted eligible women to have 6 weeks leave at 90% of their usual earning. This wasn’t expanded to all working women until 1993 as a result of a European directive
It is no coincidence that the right of women to work in professional spaces changed alongside the right of women to have representation and the right to vote. Change often comes with privilege, and not everyone benefits from the changes initially, this can be seen in some of the step wise changes above. It is beholden on those who have access via that privilege to continue the work to ensure that access is widened and available to all, rather than a select few.
What’s the Lady Mayor’s Show and how does this tie in?
The role of Lord Mayor of London has been in place since 1189 when Henry Fitz-Ailwyn first took it up, although the holder wasn’t referred to by the title of Lord Mayor until 1354. Since then there have been 697 Lord Mayors, of which only three have been female.
The first two were:
- Dame Mary Donaldson, in 1983, who famously fined people for referring to her as Lady Mayoress
- Dame Fiona Woolf, in 2013, who focused on trying to promote women into senior roles within the City of London
The role of Lord Mayor, these days, changes annually and is based upon an annual election held by the Liverymen (more on that in a separate post to come) who are members of the City of London’s Livery Companies. The process involves Aldermen presenting two candidates, followed by a vote by Liverymen to select the new Lord Mayor, who then serves a one-year term as an ambassador for UK financial services. Only sitting Aldermen are eligible for election, and so even to even be in a position to be nominated is a feat within itself, especially when many Livery Companies are still male dominated. In 2025, Dame Susan Langley was elected at the third ever female Lord Mayor.
It took until my lifetime to have a woman serve as Lord Mayor, and until 2025 to have a Lord Mayor who was happy to represent female visibility enough to call herself Lady Mayor, and set out to embrace difference in order to increase visibility and impact. The parallels between this change and some of those linked to female autonomy and role acceptance have not been lost on me. This change was celebrated as part of the annual parade at the start of the Lord Mayors term, when the parade was renamed the Lady Mayor’s Show.
As part of the principles of her term Dame Susan has focused on something called the “697 call for change” which refers to the fact that she is the 697th person to hold the office of Lord Mayor of the City of London, and the first to use the title “Lady Mayor”. This call includes:
- Adopting the Title “Lady Mayor”: While she is the third woman to hold the post, she is the first to be officially known by the title of “Lady Mayor”. This decision reflects a commitment to modernising the role and promoting diversity and inclusion within the City’s traditionally male-dominated institutions.
- The “Lady Mayor’s Show”: In another historic first, the traditional Lord Mayor’s Show was renamed the “Lady Mayor’s Show” for her procession in November 2025.
- Inclusion in the Parade: The show included 697 women from various City sectors walking in the parade with her, symbolically representing her position as the 697th holder of the office and highlighting women’s roles in the City.
- “Modern Mayoralty” Initiative: Dame Susan is committed to introducing a “Modern Mayoralty” initiative, a long-term vision to ensure the role’s ongoing relevance and to “un-square the Square Mile” by championing innovation, prosperity, and inclusion.
Having talked about historically why having women visible and in positions of influence matters to supporting changes and improvement for women more widely, the shift to clearly embracing diversity and incorporating female visibility, feels like an important declaration. It should not be a news worthy moment to include reference to Lady rather than Lord within a title, but it is indicative of a wider agenda which is significant for a role that has existed for 836 years.
Why does it matter?
We may say, well why does this matter? I certainly don’t face the same barriers as a woman of my grandmothers generation, or even those that impacted my mother. I have never been stopped from having a bank account, no one has ever stopped me having a drink in a pub. Those barriers were present in my lifetime however, and just because they are gone does not mean that other barriers do not exist. Within STEM (science, technology, engineering and maths) careers women are still under represented at senior levels, with women making up only 28% of the overall workforce in 2024. Women are still on average paid ~15% less than colleagues for the same job, and so the pay gap is certainly still present and there is still work to do.

Even in my career I have encountered numerous incidents where being a woman was included as part of a value judgement of my career trajectory, including a male colleague congratulating me when they discovered I couldn’t have children as it meant that ‘they could continue to invest in my career’ as I wasn’t going to disappear off and have children. There have been decades of my career where I was utilised to write grants and other work for my male professors, and my name was never included. Some of this is earning your way, but I am aware that there was a definite difference between how some of their male students were treated in comparison. This isn’t whinging, I found my own way. I learnt lessons. I also had the privileged (if you can call it that) to not be managing a family or caring issues which would have meant that life was harder.
This attainment difference due to lack of recognition in science linked to gender is so common that it even has a name, the Matilda Effect. This makes it even more important that women are represented at senior positions within science and tech, not just to show that it is possible, but also to change the dynamics so that some of the embedded cultural norms are subject to change.

Why did I think it was important to walk?
All of this brings me onto why I believed it was it important to walk as part of the 200 women representing science and technology. As the wonderful guys at Lead WITH Us state:
‘This isn’t just a float. It’s a signal. A collective act of visibility. 200 women. One shared purpose. Infinite possibility. A reminder that leadership takes many forms and that women are already leading, shaping, coding, building, healing, innovating, and challenging systems in ways that often go unseen.’
That was the reason that I chose to walk, but the experience was so much more than I had predicted. We walked for 3 miles along a route that was lined with people of all ages, backgrounds, and reasons for being there. The smiles of the children we encountered, the number of high fives requested and given. Walking as a group of women in science and tech, flying my geek flag proudly, being surrounded by a wonderful group of women who shared a goal and were there to support each other. Role modelling leadership in action. Hearing the cheers and feeling the welcome was an amazing reminder of the difference that science makes and how much it is appreciated.

Representation matters
The other great thing about walking with this group of women, was that the group itself was as diverse as those who lined the streets. People brought their parents, sisters, children, friends. I even brought Mr Girlymicro to help with tech and take some photos.
We come from different disciplines and backgrounds:
Some of us are Healthcare Scientist, Allied Health Professionals, nurses and clinicians working in the NHS.
Some are immersed in data and code.
Some lead strategy or drive system change.
Others are disrupting the infrastructure across delivery and design.
And some are just starting out but already creating waves.
We were walking to be visible, but more than that we were walking so others can re-imagine the future. We walked standing on the shoulder of giants who came before. Those who created a momentum. A momentum we want to continue. So much of what we do builds upon the work of those who came before.

There is still change that needs to be made. Representation still needs to be improved so that it leads to real change and that the barriers faced by those that come after us are different again from the ones that we are overcoming.
What will the legacy be?
Plenty of work will be ongoing in 2026 during this one year term and it is well worth keeping an eye on the City of London website. More than that though, there is a real hope that the 697 will become a movement and a legacy of this year. Certainly the 200 of us who walked are still linking in and a community is forming. From Whatsapp groups to a LinkedIn page, spaces are being made where we support each other, share successes, and form connections that will help everyone in their roles and ambitions. If you know a woman in Tech or Health who’s made a difference in your life or career, or if you would like to be involved yourself, then follow the links and get involved. Change can happen, but it happens best and last longest when we make it together.

All opinions in this blog are my own