Buckle up, this is a long one, but I hope you’ll enjoy reading it as much as I enjoyed writing it.
Many moons ago, I did an A-level in psychology. I enjoyed it so much that I even took some modules during my degree. During my A-levels, I still remember how much I enjoyed the section on group decision making and the different roles that both exist and can influence. During my degree, some of my favourite parts were linked to evolutionary psychology but also game theory and how mathematics and behaviour combine to impact how we should make decisions.

Now, many of you will know that I am a gamer and love all things from board and computer games through to tabletop role playing and free forming.
N.B. Some of you might not know what free forming is, so a quick description is that it is like the murder mystery games you can play, unscripted, but generally much more in depth. I like to think writing them is like writing a novel, but each character only gets their bit
Over the years I’ve had plenty of time to both write and play around within the free forming space using influencing/manipulations linked to group decision making but low and behold watching The Traitors is like all my experiments rolled into one and I LOVE IT!
What is The Traitors anyway?
For those who have managed to avoid getting hooked, first of all, congratulations, as I watch not just the British but also the overseas versions and just can’t help but get sucked in. But what is it? Launched in 2022 and is presented by Claudia Winkleman, it is a TV series where the aim of the game is to find the murderous Traitors in your group before they kill you all. Have any of you played the game Werewolf, either old school or the newer card game? At its very core, The Traitors is like werewolf with the option of extra wolves and the addition of afternoon tea.
There have now been three UK seasons, and for context, I’ve included the trailer for season one below:
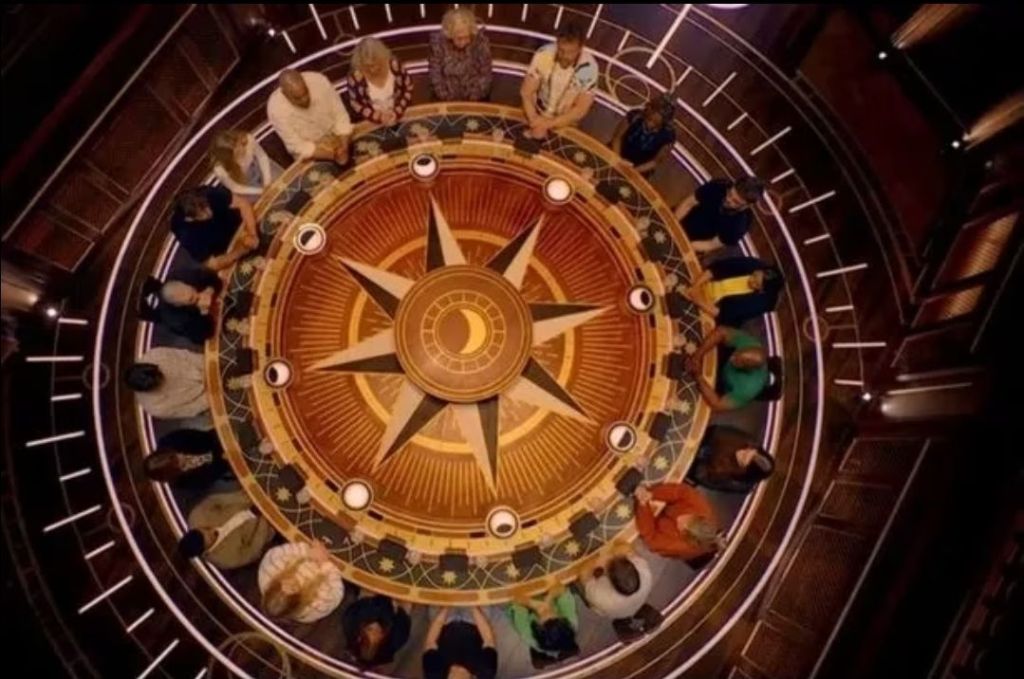
The structure goes something like this. Between 20 and 25 people arrive at a pretty glorious castle in the Highlands. On arrival they spend a day getting to know each other. That evening, they meet for a gathering around a ’round table’. Whilst blind folded, at that meeting, the Traitors (usually three) are chosen, and the game then begins. The rest of the players become what is known as Faithfuls. During the days, the group then as a whole compete to add money to the prize fund which will be won at the end of the game, and at night, the Faithfuls try to find the traitors by banishing a person they believe is part of the Traitors group. If there are any traitors left after the banishment phase, the traitors choose one person to murder. Everyone meets for breakfast the next day and finds out who is left, and the cycle begins again.
Over the next few weeks, the numbers are whittled down until there are a handful (5 ish) left. The game ends at the point the group banishes all the people they believe are traitors until there are only those perceived as Faithfuls left. They can choose to end the game at any point once down to these last few, but if, when they choose to end the game, there are any traitors left in the group, the Faithfuls leave with nothing and any Traitors split the remaining money between them.
There are only two ways to leave the show
- Banishment
- Murder
Both are based on some form of group decision making. Over the course of the game, banishment starts with a large group of poorly linked individuals and progresses to a small group of highly linked individuals in a competitive space. Whilst decisions about murder are made in a small group based on trust and risk based decision making. The dynamics of both can, therefore, change over time. To understand the challenges behind these decisions, it is key to understand that group decision making can be more nuanced and complex than it may initially appears.

Let’s talk group decision making
Two heads are better than one…..right? The basic principle of why we should use groups to make decisions is that a group will make better decisions over time than an individual alone, especially during complex decision making.
There are a number of steps that can be used to support sharing and evaluating of ideas, to support improvement in the decision making process over that available to single individuals. There are also a number of possible ways that the ‘decision’ part can be undertaken, consensus, majority, unanimity, etc. The thinking behind using these processes is that each person comprising part of the group then becomes additive, and therefore, more is better.
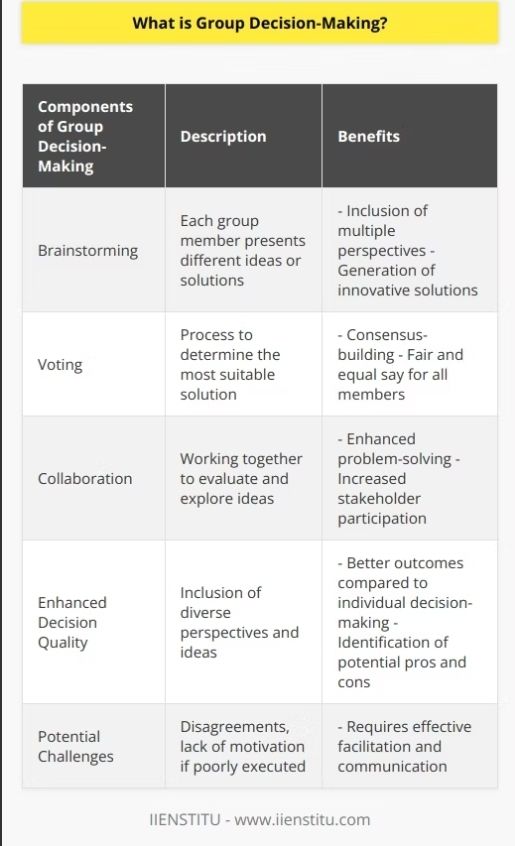
These aspects to group decision making can, if used consciously, really help bring about the most positive aspects of any decision making process. However, they all require certain things to be in place for them to actually work in the way that permits the best possible outcome, and so group decision making is predicated on how individuals work within the group to actually support its success.
What are the particular challenges of group decision making?
We all like to think that we are smart, independent thinkers who can bring something unique to the table. Partly because, as individuals, we tend to believe that we will accept and weigh all of the different perspectives that will be brought to the table equally and therefore act inclusively and positively contribute. Is this true however?
In 1981 Meredith Belbin came up with a view of how team roles. the roles that we may default into in a team, can impact how teams work and relate to each other. People generally have a preferred role that they will fall into, but roles may change based on the needs of the group and the relationships that exist, especially as these can be dictated by how the group is working.

The truth is, as demonstrated within The Traitors, we don’t necessarily value all of these roles equally. Within The Traitors, often the people centred roles are valued more highly, especially early on, and so people who are ‘different’ such as plants or ‘challenging’ such as shapers may be prone to banishment early in the process rather than being valued due to the different perspective they bring. Other roles, such as the implementer or monitor evaluator, may become isolated as too focused on task and therefore ignore the social niceties required to build social capital, which is important to be able to call on when you inevitably come under suspicion.
We see those not like us as being a source of risk or difference that can lead to distrust, which makes those that could be highly valuable, linked to their differences in perspective or approach, actually to be seen as individuals to remove from the group early. Thus making the whole task of finding the Traitors to actually become more inefficient early in the process. These challenges aren’t just present in The Traitors decision making though, and so Belbin encourages self reflection to understand the roles we take and what benefits and disadvantages they hold.
How does voting impact and a lack of facilitation impact?
We often like to think that we are useful and can actively contribute. In the case of The Traitors, participants like to believe that they know, or can spot things that others cannot, and therefore can make themselves valuable members of the group. For the Traitors, all scenarios will feel like a risk as we like to believe that others are as obsessed with us as much as we are focused on ourselves, something called the Spotlight Effect. In recent seasons, there has also been a focus from the Faithfuls on obsessing about why they have been kept in and not murdered, hence placing increased focus on themselves and the importance they play within the group. All of this plays out around the round table linked to the fact that a single round of majority voting is utilised in order to enable the group to make a decision.

Other types of voting would have different impacts on the group and how they made decisions, but may not be as dramatic, and in most cases would take longer. The issue with many of these other types of voting is how dissent and intransigence is managed in order to move discussions forward and ensure that the beneficial aspects of group decision making are actually realised.
One of the reasons that these alternate methods would be challenging, even if included, is that they really rely on facilitation in order to work. In The Traitors, there is no external group facilitation, all roles are held by people in group who are driven by both group and individual needs and have an embedded interest in the selected outcome. The host acts merely as a neutral observer to the process. If setting up your own group, evaluating the success of groups you are part of, or thinking about processes, it is worth being aware of how decision making tools influence both group behaviour and group effectiveness, and ensure that the right structures are put in place to support both.
Why can the voting shift so rapidly?
As the Faithfuls become more developed as a group, or at any point where they feels like there is a dominant voice/person demonstrating confidence in their opinion, it can be surprising how quickly the conversations and prior decisions made before going into the round table can change. There is usually plenty of hanging around and talking during the day, where people get to know each other, voice suspicions, and try to capture evidence, which is usually in limited supply. The number of times this happens, and someone sounds like they are doomed to be banished, then everyone sits around the round table and suddenly everyone is voting for someone else entirely may appear surprising, but how often is group decision making truly group decision making? How often does it become the echoing of a dominant voice?

What is group think?
Groupthink was first coined as a term in 1952 but the first real published book investigating it was published by Janis in 1972.
Groupthink is a phenomenon that occurs when a group of well-intentioned people makes irrational or non-optimal decisions spurred by the urge to conform or the belief that dissent is impossible
The need to be part of the majority when voting, the need to be seen to be part of the consensus, makes the voting process and group decision making in The Traitors particularly at risk of Groupthink. This is where the desire for group consensus and harmony leads to poor decision-making. Within the round table at the traitors, especially at the start, no one wants to draw attention to themselves. You want to be middle of the road initially, as you neither want to draw the attention of the Faithfuls, thus standing out and being at risk of banishment, or of the Traitors, putting yourself at risk of murder. No one wants to be an outlier.

As time goes on, and the numbers decrease, individuals need to be seen to have a voice as not having an opinion increasingly raises suspicious. At the same time, there always seems to be a couple of players who become dominant, often due to the random luck of having found a Traitor previously, and are seen as being somehow more competent to find Traitors than others. Groupthink therefore definitely starts to play a more significant role in the middle stages of the game due to the changes group dynamics. How this Groupthink plays out can happen in a number of ways from collective rationalisation during discussions that one person is definitely a Traitor, normally based on fairly flimsy evidence, to some people being almost immune to accusations as they have come to be seen as such good Faithfuls, for equivalent light levels of data. It is often only when players reveal whether they are actually Faithful or Traitor, when banishment decisions have been made, that some members will then voice the fact that they didn’t support the wider decision or that they wish they had had the capacity to speak up.
The other interesting thing that comes into play during round table discussions, is that there are obviously traitors who are deliberately muddying the waters or throwing in dissent in order to disrupt the group decision making process. These members act like ‘mindguards’ who are group members that limit information and control dissent to influence the decision-making process. It is interestingly not only the Traitors who do this however, in varying seasons there have also been cliques that develop who have also acted in a similar way, but claim it is to protect themselves and improve the ability to identify those they perceive as untrustworthy. This tends to benefit the individuals but does not necessarily act to benefit the group as a whole, in terms of decision making quality.
Let’s talk treachery
The show wears its truth on its sleeve, it is called The Traitors after all. Trust plays a fundamental role in both individual relationships and on group dynamics. Therefore the role of trust and how this level of trust varies across the period of the show is an essential part of the entertainment factor and impacts on how successfully the group complete the given task of trying to find the Traitors in their midst. In a normal setting, trust is built over time as the group establishes itself. In the case of The Traitors, this process deliberately erodes trust, as the more the group establishes the smaller it becomes, and it becomes more likely that the person you are left talking to is actually a traitor whose considering your death. All of this leads to an ever building sense of paranoia.

The other reason that paranoia can be rife is that the role of Faithful is not static. You could therefore be sure that you had a relationships with someone based on the fact that they were ‘clearly’ Faithful, but it is possible that something could happen which means that they changed from being a Faithful to a Traitor during the course of the game. There are also moments when new group members are added later on, which means that members, and the group as a whole, lose their equilibrium and then need to re-establish. This also means that those players who are introduced later can also struggle to ever be seen as part of the group in the same way as the original players.
The reasons that players can change to become Traitors are three fold:
- Original selection as a Traitor on day 1 (change from unassigned to Traitor)
- Seduction – if a Traitor is banished, the Traitors can choose to recruit from the remaining Faithfuls. The Faithful can choose to join or refuse, but often even admitting that someone has tried to recruit you can lead to an increased risk of banishment
- Ultimatum – if at any time there is only one Traitor left in the game, the remaining Traitor selects on member of the Faithful and they are given an ultimatum. They can either join the Traitor or they will be murdered. Needless to say, under these circumstances players almost always choose to join rather than die. This can impact dynamics later however and mean that the ‘forced’ Traitor may be more likely to turn on their fellow Traitors
The Traitors therefore have their own group dynamics that are playing out in secret amongst all of the dynamics of the wider group. All of which can impact how wider decision making processes occur, as some individuals may choose to sacrifice a Traitor to the wider group in order to establish themselves as more trusted or to change group dynamics.

So what is game theory and how does it apply here?
All of this brings us to game theory, and more specifically to the Prisoner’s Dilemma
Game theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with the analysis of strategies for dealing with competitive situations where the outcome of a participant’s choice of action depends critically on the actions of other participants.
When The Traitors is described as a game, it very much is, both as a whole and with every single decision made. The Traitors within the group are playing something called the Prisoner’s Dilemma, pretty much throughout as they decide every round table whether to support each other or sell each other out. At the end game, however, everyone ends up playing this particular example of game theory, whether they are a Traitor or a Faithful, as banishment’s continue until everyone believes there are only Faithfuls left.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma is described like this:
The classic prisoner’s dilemma goes like this:
- Two bank robbers, Elizabeth and Henry, have been arrested and are being interrogated in separate rooms.
- The authorities have no other witnesses, and can only prove the case against them if they can convince at least one of the robbers to betray their accomplice and testify to the crime.
- Each bank robber is faced with the choice to cooperate with their accomplice and remain silent or to defect from the gang and testify for the prosecution.
- If they both co-operate and remain silent, then the authorities will only be able to convict them on a lesser charge resulting in one year in jail for each (1 year for Elizabeth + 1 year for Henry = 2 years total jail time).
- If one testifies and the other does not, then the one who testifies will go free and the other will get five years (0 years for the one who defects + 5 for the one convicted = 5 years total).
- However, if both testify against the other, each will get three years in jail for being partly responsible for the robbery (3 years for Elizabeth + 3 years for Henry = 6 years total jail time).

Therefore the best move, for either Elizabeth or Henry is to defect, as this is the move with highest payoff, either because they both defect, in which case they only serve a year in jail, or because the other person doesn’t, in which case they walk away completely free and the other person pays the entire cost. This is what is known as the Nash equilibrium, where both parties should defect in order to maximise their individual benefit.
Within the context of The Traitors, this means that at some point, when the heat is on your fellow Traitors too much, you should join the rest of the group in order to banish them as a Traitor in order to validate yourself as a Faithful. It also means that during the end game phase, when players can continue to banish down until they reach the final 2, as long as you are sure that you are not one of the ones at risk of banishment, you should always continue to decrease the group to the smallest numbers possible in order to try to ensure that no Traitors are left. It is the balancing that with your individual banishment risk that is the biggest challenge however. When there is money at stake, when there is an actual individual cost to decision making, then the maths is clear about what you should do next.
What does all of this teach us, and how can we apply some of what we’ve learnt?
Apart from being a cracking piece of entertainment, I hope that this post about The Traitors has made us think that group decision making may not be as simple and issue free as we sometimes like to believe. There are a number of actions required of us as individuals in order to make it an group decision making the improved option, and a lot of individual responsibility that must not be forgotten as part of becoming a collective. When undertaking your role as a decision maker within a group setting it is worth being aware of the need to:
- Self reflect on the roles you take when in groups, especially how these change depending on stress levels and how comfortable you are with other members
- Actively evaluate how well your group decision making processes are supporting or impeding the effectiveness of the decisions
- Not just default to majority voting because it is a) what you are most familiar with or b) quickest and perceived as easiest
- Think about when to use facilitation to improve the quality of any group actions
- Be aware of groupthink and attempt to have measures in place in order to reduce its impact
- Know that, if the individual costs and consequences are high enough, the best mathematical choice is to defect (I say this tongue in cheek in terms of the maths, please also remember the human cost in any decision making)
Anyway, season 3 of the US version of The Traitors is just dropping now on BBC iPlayer, and so I’m off to see whether my thinking holds even if there are cultural differences. Just to finish though, I’d also like to end with flagging one of the best film examples of group decision making and how group dynamics can be utilised to impact outcomes. If you’ve never seen 12 Angry Men, it’s a masterclass, and I’d highly recommend you take some time out of your life to check it out and to think how you might respond if placed in a similar situation.
All opinions in this blog are my own
